PHP Luminova: Page Caching & Static Content
Optimize page delivery with cached content. Store and reuse pages for faster load times, supporting static URLs, file extensions, and versioned caching.
The Luminova template content cache is a built-in system that allow you to cache the final output of a page and serve it like a static file. It works with URLs that end in an extension (such as .html) or URLs without an extension. If a URL has no extension, the request goes through your controller first. This allow you to inspect the request, modify the content, reuse an existing cached version, or let Luminova decide whether to serve the cached output or rebuild the template.
How It Works
When a page is requested, Luminova checks whether template caching is enabled. If it is, the generated content is saved for future use.
By default, cached files are stored under:
/writeable/caches/default/You can change this directory inside your App\Config\Template configuration class.
Cached content is grouped into folders based on your application app.version. This is useful when your site uses versioned paths, common in docs and API guides websites. When you publish a new version, older cached pages remain available, avoiding unnecessary 404 errors for users browsing older documentation.
Cache Performance Testing
These tests compare page load performance under different caching scenarios in Luminova.
1. Content Caching DisabledNo caching is used; the page is rendered fully on each request.

Execution: 96.41 ms | Database: 11.92 ms | Memory: 2.61 MB | Files: 58
2. Regular Content Cache RenderingPage content is cached after the first request, reducing database queries and execution time.

Execution: 26.61 ms | Database: 0.00 ms | Memory: 1.26 MB | Files: 38
3. Static Cache Extension Suffixing RenderingUsing a static file extension (e.g., .html) bypasses controllers and middleware, serving content almost instantly.
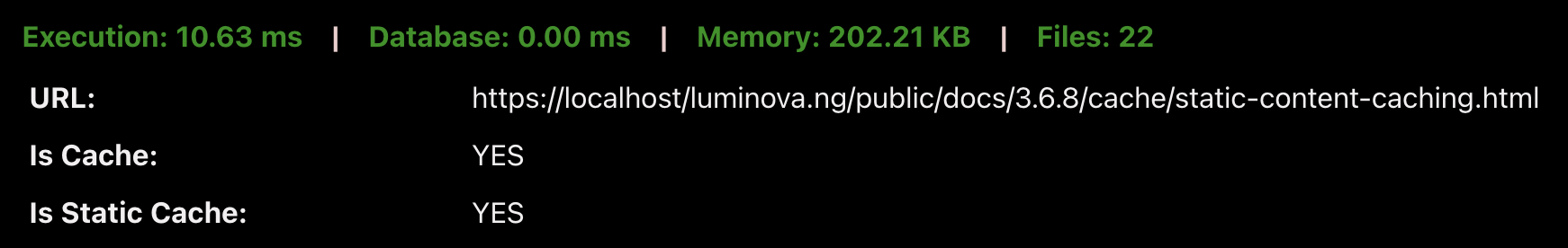
Execution: 10.63 ms | Database: 0.0 ms | Memory: 202.21 KB | Files: 22
Comparison:
- Enabling regular caching already cuts execution time by ~3.5×.
- Using static cache extensions further reduces execution time by ~9×, lowers memory usage, and decreases file loads.
- Static caching is ideal for pages that rarely change and are accessed frequently.
Page Cache Setting
Several environment variables control how the cache behaves:
Enable Page Caching:Set
page.cachingtotruein your.envfile to activate page caching.Choose Cache Directory:If needed, update the cache storage path in your application’s Template configuration class located at
/app/Config/Template.php.default.cache.controlDefines the
Cache-Controlheader sent to the client.page.cache.expirySets how long cached pages remain valid before they are refreshed.
page.cache.app.versionsAllows Luminova to serve cached pages from older application versions.
page.cache.latest.contentAllow you to specify array of URI patterns that should always use the latest application version when caching.
page.caching.uri.queryControls how Luminova builds cache keys from URLs. When enabled, query parameters (for example,
company/about?foo=bar) create separate cache entries. When disabled, all variants are treated as the same URL (company/about).
Together, these settings give you flexible control over how pages are cached, reused, and refreshed across different versions of your application.
Cache Versioning
Luminova supports version-controlled caching. This allow the framework to serve cached content from older application versions when the current version has no matching cache. You enable this by listing older versions under page.cache.app.versions.
For example, if your current app version is 1.2.0 and you still want to serve old caches under 1.0.0 and 1.1.0.
Example:
This tells the caching system to fallback to those versions when needed.
page.cache.app.versions = [1.0.0, 1.1.0]https://example.com/1.0.0/aboutandhttps://example.com/1.1.0/about— each serves the correct versioned content.https://example.com/1.2.0/about— always serves the latest version’s cache.
Note:Versioned caching works best with versioned URLs.Non-versioned paths (like
/about) always return the latest version because the cache key never changes.
Cache Priority Version
You can also define URI patterns that should only use the latest version’s cache. Add these patterns to the page.cache.latest.content.
Example:
page.cache.latest.content = ['/', 'blog', 'blog/*/foo', 'foo/*']The framework then searches for cached content for these paths only in the current version’s cache directory.
Non-Expiring Content
Luminova allows you to create static content that doesn’t expire by configuring the cache and HTTP headers correctly. To do this, set page.caching.immutable to true in your environment configuration. This tells browsers to cache the content for a long period, based on page.cache.expiry, and the immutable directive ensures the content won’t be revalidated during that time:
Examples:
Set cache immutable variable to true:
page.caching.immutable = trueThe HTTP header will look like:
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutableset page.cache.expiry to 0 (or a very high value) to prevent the cache from being cleared:
page.cache.expiry = 0For assets like images or CSS that you want to cache indefinitely, it’s recommended to use versioned URLs. Appending a version number to the file name, path or query parameter (e.g, ?version=<?= APP_VERSION;?>), ensures that browsers fetch updated content when it changes, while older versions remain cached:
<img src="<?= asset('images/v-' . APP_VERSION . '/logo.png'); ?>" alt="Logo">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<?= asset('css/v-' . APP_VERSION . 'styles.css'); ?>">Finally, configure your web server to serve these files with a long-term caching strategy.
For example, in Nginx:
location /static/ {
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=31536000, immutable";
}With this setup, Luminova serves static content efficiently, keeps it cached for a long time, and allows safe updates using versioned assets.
Static Cache URL Extension Suffixing
By appending extensions to URLs when caching is enabled, Luminova can serve content as partially static. In this mode, only the framework’s autoloaded modules and Luminova\Cache\StaticCache are loaded before serving the cached page. Controller methods and other modules are skipped, which can reduce view response time by up to 30% compared to standard caching without a URL extension.
Static Caching Setup
Static caching in Luminova works by associating cached pages with specific file extensions. To enable this, define the allowed extensions in page.caching.statics. Multiple types can be separated with a pipe |:
page.caching.statics = html|jsonCommon Types:
html, json, txt, xml, rdf, atom, rss, css, js
Note:Luminova can cache any content type the browser can render.The types listed above are just the defaults within view class.
Controller Examples:
The extension you define must match the type used when rendering the view via the Luminova\Template\View class methods.
namespace App\Controllers\Http;
use Luminova\Base\Controller;
use Luminova\Attributes\Route;
use Luminova\Attributes\Prefix;
#[Prefix('/(:base)')]
class MainController extends Controller
{
#[Route('/page')]
public function htmlView(): int
{
return $this->view('home', type: 'html'); // Or View::HTML
}
#[Route('/page/style')]
public function cssView(): int
{
return $this->view('style', type: 'css'); // Or View::CSS
}
#[Route('/page/settings')]
public function jsonView(): int
{
return $this->view('settings', type: 'json'); // Or View::JSON
}
}After defining the allowed types, append the corresponding extension to your request URL.
For example, using .html to serve static contents immediately:
https://example.com/page.html
https://example.com/page/style.css
https://example.com/page/settings.jsonThis tells Luminova to check for a cached page first. If a valid cached version exists, it is served immediately; otherwise, the page is rendered normally and the compiled content is stored for future requests.
Cache Extension Suffixing Examples
For a blog page at:
https://example.com/blog/how-to-install-luminovaAppending .html serves it as static content:
https://example.com/blog/how-to-install-luminova.htmlIf a cached version exists, it loads instantly. If not, the page is rendered normally and the compiled HTML is saved.
Accessing the page with an unsupported extension, like:
https://example.com/blog/how-to-install-luminova.jsonwill fail unless a .json version is provided in your controller.
Caching Conflicts with Error Pages
Sometimes a cached page can be mistakenly replaced by an error page.
For example, if you visit (https://example.com/page/action/about.json), and it triggers a 404, Luminova may cache the 404.php page using the same key as the intended page (about or about.html). This will happen because URL-based cache key doesn't use extensions when hashing cache keys.
Effect:Subsequent visits to:
https://example.com/page/action/about
https://example.com/page/action/about.htmlmay serve the cached error page instead of the correct content.
Bast Practice:
When using a custom error page or password protected pages, that you renders manually based on certain conditions, ensure that this page are excluded from caching.
Preventing Error Pages from Being Cached
To avoid this, exclude error pages from caching. You can do this globally in your application:
namespace App;
use Luminova\Foundation\Core\Application as CoreApplication;
class Application extends CoreApplication
{
protected function onCreate(): void
{
$this->view->noCaching([
'404',
'4xx',
'5xx'
'error',
'login'
]);
}
}Tip:You can also disable caching for specific pages within a controller before rendering:
$this->tpl->noCaching('error');
Important Limitation
When a specific .extension is appended to a view request URL (e.g., .html, .json), Luminova treats the request as static content. As a result, application events, middleware, and after-middleware will not be executed.
Note:
This is intentional. Treating the request as static ensures the cached version is optimized for speed and performs better than a non-static cache request.
Canonical URL for Static Pages
Adding a canonical link tag to your pages helps search engines identify the preferred URL, preventing duplicate content issues when multiple versions of the same page exist. For static cached pages, include the canonical URL in the <head> section of your page.
Examples:
If you are using luminova structured data embedding module:
// /app/Application/php
namespace App;
use \Luminova\Components\Seo\Schema;
use \Luminova\Foundation\Core\Application as CoreApplication;
class Application extends CoreApplication
{
/**
* @var Schema|null $Schema;
*/
public ?Schema $schema = null;
protected function onCreate(): void
{
$this->schema = new Schema();
$uri = $this->getUri();
$this->schema->setUrl(APP_URL, $uri);
$this->schema->setCanonical(APP_URL . $uri);
if($uri){
$this->schema->setCanonical(APP_URL . "{$uri}.html");
}
}
}Then In Template
<head>
<?= $this->app->schema->getHeadTags();?>
<?= $this->app->schema->getJsonLdScript();?>
</head>Result:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/blog/how-to-install-luminova"/>
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/blog/how-to-install-luminova.html"/>In this example, both the standard URL and the .html static version are shown. Using a canonical tag ensures search engines index the correct URL for your content.
How Luminova Stores Cached Content
Luminova’s caching system stores pre-rendered page content along with metadata to deliver pages quickly and reduce server load. Each cached page includes information like Content-Type, Expiry, ETag, and whether the cache is immutable.
When a page is requested, the framework first checks the metadata to see if a valid cached version exists. If it does, the cached content is served immediately, skipping the normal rendering process. If the cache has expired or is invalid, the page is rendered normally and stored for future requests.
Benefits of This Approach
- Faster Page Loads: Serving pre-rendered content reduces server processing time.
- Flexible Cache Control: Metadata like
MaxAgeandCacheImmutableallows fine-tuned control over caching behavior. - Optimized Performance: Frequently accessed pages that rarely change benefit the most, improving overall site speed and reducing server load.
This mechanism provides a balance between performance and control, making Luminova caching suitable for both static pages and dynamic content that needs occasional updates.
